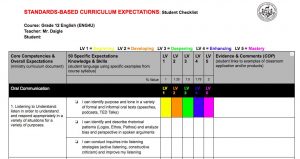
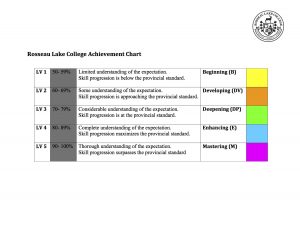
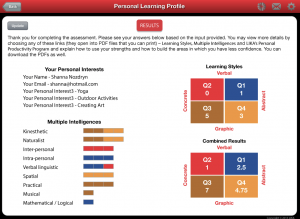
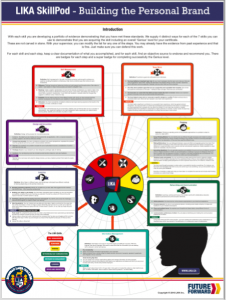
After witnessing the impact Cohort21 has had on its many participants over the years, I found myself in a conversation at our 3rd F2F (Season 8) with Lincoln Smith (@lsmith), about how to help teachers recognize their own ability to transform their practice. It occurred to me that even though I had taught public school in Australia for 7 years, and have now taught in private schools in Canada for a further 5 years, it wasn’t until Cohort21 that my inner innovator was unleashed. Huge gratitude must be shared with @gnichols and @jmedved for modelling the type of collaborative, initiative-seeking mindsets in their PD’s, that first set me on a path to rethinking education. Cohort21, and its many passionate alumi innovators (@lmcbeth, @ddoucet, @timrollwagen, @adamcaplan, @shelleythomas, @brenthurley, @gvogt, @egelleny) provided me with the necessary permission to take disruptive risks in my own teaching practice. Seeing how hindsight is 2020, it makes sense to look back as I also look forward to my riskiest venture yet— my new future as co-founder of my own innovative high school, SiTE Schools Dundas.
The following is a list of common sense changes to secondary school education, if we are looking to represent adolescents in a more dignified and developmentally appropriate way. Many colleagues (@nblair, @tjagdeo, @ljensen, @mhodal, @acampbellrogers, @amacrae, @eoboyle, @lmustard, @tfaucher, @jsheppard, @lmitchell, @bblack, @estewart, @mbrims, @wdarby, @lbettencourt, @rabbiento, @elee) were asking me if I have started recording the pedagogical innovations on my journey. I have no doubt there will one day be a book. For now, this blog (now in its entirety, with further resources at the end) is a start in that direction. The new Montessori high school (SiTE Schools) I have co-founded with Tony Evans, is proof that truly engaging alternatives to mainstream education exist.
1. Small Class Sizes
Every educator knows the secret ingredient of teaching lies in the relationship formed between pupil and teacher. This can be a whole class relationship or one-on-one. Both are vital. Yes, some studies suggest class size does not make a marked difference to academic achievement at the secondary level. But it never hurts. I’ve yet to see a student or parent complain of too few classmates. In my experience, the optimal class size sits somewhere between 10–16. Less than that and you may find it hard to motivate, initiate discussions, or form dynamic groupings. More than that and you inevitably have students who hide, succumb to distraction, or fall through the cracks — making it impossible to personalize learning and create meaningful connection. Class size is the silver bullet of education reform. Teachers and students and parents agree. It is more fundamental than resources or buildings or curriculum, and has the ultra-cool added benefit of providing more jobs.
2. Mixed-Age Groupings
Having a balance of multi-age students in a classroom not only helps with peer tutoring and mentorship, you simultaneously vanish the stigma of both underachievers and overachievers. You also provide authentic extension material for those students ready to move through the course at a faster pace (which can and should include moving to the next grade), and you erase the arbitrary notion of age being the determining factor of ability. The Montessori framework preferences a 3-year age grouping, which works well in an adjusted high-school arrangement of Grades 7–9 and 10–12. Students in these scenarios very quickly forget their age differences and become more interested in sharing knowledge and gaining experience. For a student moving through these levels, this means at least two opportunities to review and understand the material with peers and a further opportunity to teach it to the class; which is the ultimate form of education, allowing the teacher to take the necessary step back and get out of the way of the learning.
3. Purposeful Work
We know that what often drives us in our lives are those moments when our passions produce “flow states”, described as when time becomes insignificant, the work we do, joyful. Are teenagers any different? Perhaps they are even more drawn to this way of being. They crave meaning in their lives at the exact time when their quest for identity has hit its stride, when the questions of difference between themselves, their parents, or other social groups is all encompassing. If high schools don’t answer this call to action, if they don’t provide authentic academic experiences that relate to student interests and have real-world consequences, then they have failed adolescents. If knowledge content becomes diminished at this stage, so be it. Social-emotional learning (SEL) and social justice appeals have proven to be more significant and will help teenagers gain the self-confidence that will foster intrinsic motivation towards lifelong learning. We know that resilience comes from overcoming challenge and failure. So challenge them, and let them fail.
4. Meaningful Context
Why are we learning this? This may be the only question worth asking in the information age. If today’s teacher can’t answer this in a practical way, it’s fair to say that subject’s easy-to-search content should not be taught. Contextual learning can come in many forms; you can teach the history of math, uncover local environmental issues, or invite experts. Teachers should be trained to relate popular culture, current events and the latest innovations, into a classroom discussion to build engagement through mutual relevance. What you should never do is plan your entire lesson in advance, because context is like live theatre: it only works in the moment and will change from class to class and year to year. Overplanning for the sake of admin compliance is not only a recipe for teacher stress and anxiety, it actively works against the needs of adolescents. A teacher who is unable to observe the mood and interests of the class and improvise with their subject material, is not modelling the very flexibility we are asking the students to develop.
5. Learning Happens Everywhere
Too often, high schoolers spend their days shuffling from one uninspiring classroom box to another. Small respites can be found at lunch or during spare. Increasingly, even these breaks are becoming pressured into further programming such as wellbeing training. What effect does this have on the autonomy of the adolescent who is entirely shaped by their environment? How do they perceive scholastic institutions when everything is institutionalized? What if learning could happen anywhere and the separation between the real-world and the school-world wasn’t so defined by the boundaries of property. Adolescents must connect to this outside world and a new definition of community: projects, publishing, protesting, presenting — however and whenever there is more at stake than a mark. Co-ops, internships, and service should be compulsory. An abundance of connections exists through any parent community. If churches produce reverence, museums a sense of wonder, galleries artistic appreciation, then what are schools built for?
6. Question, Discuss, Repeat
Maria Montessori refers to the 3rd Plane of Development, the stage known as adolescence, as the time when the youth becomes a “social newborn”. It goes without saying, then, that a large amount of this time is set aside for talking with peers; talking about relationships, talking about problems, about dreams, hopes, frustrations, absurdities. The role for adults at this stage is to listen without judgement, observe and guide where appropriate. The role for teenagers is to ask great questions. This is in fact the only way to check one’s ideas and ideals. In a properly curated discussion, where respectful communication is modelled, the most amazing epiphanies and analogies will spontaneously arise. Deeper learning will flow from inquiry, dialogue will become discourse, provocations will lead to new perspectives. Call it Socratic seminar, Harkness method, classic debate — what matters is there is space for everyone to be heard. Discussion is the first, best, and last method of education. Best of all, it does not require wifi!
7. Less Rubrics, More Resilience
Current pedagogical practice will tell you the more scaffolding and transparency you provide a student, the greater chance they may have to satisfy assignment expectations. They’ve even given it a name — universal design for learning (UDL). What they don’t tell you is how this very strategy also reduces creativity and originality as youth limit themselves to imitate exemplars instead of reaching towards a unique product. I’ve seen it too often, where teenagers ask what it takes to get a 90% rather than asking how they can tailor their personal interests into a project that satisfies the criteria. When we consider the rise of learning difficulties experienced by students today, and the overall lack of resilience and adaptability found as a result, do we not need to look at ourselves as educators and find our own heavily administered practice culpable? Find as many ways to co-construct assessments as possible. Have adolescents write their own reports. This isn’t sidestepping your duty, it’s allowing them ownership over theirs.
8. Go Gradeless Already!
Process over product. Formative versus summative. Ongoing checkpoints as opposed to strict outcomes. Stop the debating and give adolescents and parents the only solution proven to decrease anxiety and stress. The minute you remove standard numerical assessment, the sooner you see teenagers learn for the sake of learning. The minute you dissolve arbitrary deadlines, watch as youth become negotiators of their own work habits. When you give constructive feedback instead of points, observe how students will spontaneously do another draft to correct their mistakes and appease their own growing success and worth. Because what it comes down to is, what is the self worth? It may take many years for grades to cease being the benchmark for post-secondary acceptance but these numbers don’t have to be shared with students now. The increasing trend of skills-based reports and project portfolios — applications preferencing experience — suggests it won’t be long before what we measure is the capacity for being open to learning and not the learning itself.
9. Freedom to Teach
Teaching is an artform. The development of one’s individual style and voice is the career goal. Despite attempts for schools to carry on popular programs when a revered teacher leaves, something is always lost in the absence of a great educator. This is because at its core, teaching is an individual practice, separate from the mission statements of boards and curriculum standards of ministries. Teachers facilitate with dynamic personality and accumulated experience; the more they have of both these traits, the better they usually fare in this most noble of professions. Principals and department heads would be wise to heed this advice: let your teachers follow their bliss and watch as their students likewise become more open minded and curious individuals in the face of such passion. As soon as teachers become bogged by administrative duties, caught in union politics, or are viewed as less important than alumni or parents, you have limited society’s most vital resource for transmitting Enlightenment values.
10. Think Outside the Domain
“Modern life requires range, making connections across far-flung domains and ideas.” (David Epstein, Range) By the time students reach secondary school they have already been standardized into the narrow structures of subject-specific thinking. For many, English and Math seem separated by gulfs of unbridgeable content. Yet if we simply renamed these traditional disciplines, say, Communication or Problem Solving, we might suddenly see just how connected they are in terms of broad application. Adolescents feel pulled in a thousand directions by the various methods subjects silo them into. This can easily be changed by focussing on each subject for an immersive period of time instead of grazing superficially. What if teenagers could master skills and mindsets in each discipline before moving to the next one? What if these transitions were not arbitrary, but curated, to allow an understanding of subject similarities instead of emphasizing differences. You don’t take an Uber to the “science” part of town. All knowledge is transformational and integrated.
 Photo by Lindsay Palmer | http://lindsaypalmer.ca/
Photo by Lindsay Palmer | http://lindsaypalmer.ca/
11. Dignity is Not a Four Letter Word
Adolescents are ready for the adult-world but they feel a great amount of unrest about this burgeoning responsibility. In another time and place they would have already been part of the workforce, helping out on the farm, married, or fighting in a war. Their passion and energy for life is unmatched and has the capacity to start revolutions or go viral. Look at the great work of climate activist, Greta Thunberg. She is respected because of her unique perspective; she has not compromised her values for an adult rationalization of how the world works. Self-determination is the result of feeling individual worth. This is not some small measure of character but rather a developmental necessity for growth and dignity. If you lend adolescents a sense of autonomy and self-direction through voice, choice, expression, and movement, you will earn that same dignity back. This two-way street is the rough pavement our teenagers tread. Uncertainty breeds opportunity. Adolescence is a time when you get fired by the boss and hope you get hired back on as a consultant.
12. Actual Critical Thinking
Perhaps the most overused and underdeveloped term in education. Very simply, critical thinking is the ability to recognize what is not being said in any given situation. It was developed by the Frankfurt School of German philosophers escaping to America during WWII. Determined to never let a totalitarian regime happen again, they rallied against the status quo by questioning all of society’s codes and conventions. If education is based on liberal values, on the emancipation of the individual becoming a more informed and productive citizen, then this skill of discernment is primary. It should be explicitly developed through credible research and metacognition. Thinking about thinking is a powerful way for adolescents to move beyond a black and white view of the world. By embracing paradox, challenging bias, dissecting mental models, and confronting counter-intuitive scenarios, youth learn to hold space for meaningful reflection. This is why, as Montessori said, “establishing lasting peace is the work of education, all politics can do is keep us out of war.”
13. Nature is Nurture
Get outside, more often. Or as Richard Louv, author of Last Child in the Woods says, “school isn’t supposed to be a polite form of incarceration, but a portal to the wider world.” This generation is driven by a social and moral imperative to help save our planet from climate change. High schools should provide experiential situations where this passion for sustaining the natural can be fostered. Again and again. Despite all the advantages our amazing technologies can provide, we must do more as humans to embrace deep ecology. Educator Mitchell Tomashow says, “the ability to conceptualize environmental issues on a global scale, one must first have the trained skills to observe the details of local interrelationships, relationships that one can actually perceive with one’s own senses.” Teenagers need to work with their hands, build up, dig down, use tools, investigate, and reaffirm their relationship with nature through a renewed respect of place. Every school should be a forest school.
References
1. Small Class Sizes
Allison, Derek J. Secondary School Class Sizes and Student Performance:
Alphonso, Caroline. Does Class Size Matter? Many Teachers are Adamant it is Crucial: https://www.theglobeandmail.com/canada/article-does-class-size-matter-many-teachers-are-adamant-it-is-crucial/
2. Mixed-Age Groupings
Three-Year Age Spans in Montessori Classrooms: https://www.public-montessori.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/Three-Year-Age-Spans-in-Upper-Elementary.pdf
3. Purposeful Work
Oppland, Mike. 8 Ways to Create Flow: https://positivepsychology.com/mihaly-csikszentmihalyi-father-of-flow/
Weissberg, Roger. Why Social and Emotional Learning is Essential for Students: https://www.edutopia.org/blog/why-sel-essential-for-students-weissberg-durlak-domitrovich-gullotta
4. Meaningful Context
Andriotis, Nikos. Contextualised Learning: Teaching Made Highly Effective: https://www.efrontlearning.com/blog/2017/06/contextualized-learning-effective-elearning.html
Pg Hj Besar, Dk Siti Norainna. Situated Learning Theory: The Key to Effective Classroom Teaching: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327530821_Situated_Learning_Theory_The_Key_to_Effective_Classroom_Teaching
5. Learning Happens Everywhere
Martinez, Monica. Four Practical Steps to Deepen School and Community Connections: https://medium.com/xqamerica/four-practical-steps-to-deepen-school-community-connections-ddcc921b00bf
O’Keefe, Brendan. 5 Steps to Better School/Community Collaboration: https://www.edutopia.org/blog/school-community-collaboration-brendan-okeefe
6. Question, Discuss, Repeat
Andrews, Sarah Werner. Montessori Institute Northwest. Four Planes of Development: https://montessoritraining.blogspot.com/2007/07/montessori-philosophy-third-plane-of.html
7. Less Rubrics, More Resilience
Morin, Amanda. Universal Design for Living (UDL): What you Need to Know: https://www.understood.org/en/learning-thinking-differences/treatments-approaches/educational-strategies/universal-design-for-learning-what-it-is-and-how-it-works
Reuser, K. Co-Constructivism in Education Theory and Practice: https://www.ife.uzh.ch/dam/jcr:00000000-3212-6146-0000-00004ae1a3f6/Co_Constructivism.pdf
The Education Hub: https://theeducationhub.org.nz/how-to-help-students-improve-their-resilience/
8. Go Gradeless Already
Whitmell, Terry. More Teacher Are Going Gradeless. I Asked Them Why: http://www.ascd.org/ascd-express/vol14/num31/more-teachers-are-going-gradeless-i-asked-them-why.aspx
9. Freedom to Teach
Sinclar, Ashley-Lamb. Why Teachers Need Their Freedom: https://www.theatlantic.com/education/archive/2017/09/why-teachers-need-their-freedom/539151/
10. Think Outside the Domain
Edutopia. Why Schools Should Embrace Integrated Studies: https://www.edutopia.org/integrated-studies-introduction
Epstein, David. Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World: https://www.davidepstein.com/the-range/
Quest University. The Block Plan: https://questu.ca/academics/the-block-plan/
11. Dignity is Not a Four Letter Word
Ark, Tom Vander. Developing Self-Directed Learners: https://www.gettingsmart.com/2016/12/developing-self-directed-learners/
Casey, BJ. The Storm and Stress of Adolescence: Insights from Human Imaging and Mouse Genetics: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2850961/
Saxelby, Meaghan. Bring Dignity Into Your School and Transform Culture: https://culturesofdignity.com/bring-dignity-into-your-school-and-transform-culture/
12. Actual Critical Thinking
Duckworth, Cheryl. Maria Montessori’s Contribution to Peace Education: https://www.tc.columbia.edu/epe/epe-entries/Duckworth_ch4_22feb08.pdf
Illing, Sean. If You Want to Understand the Age of Trump, Read the Frankfurt School: https://www.vox.com/conversations/2016/12/27/14038406/donald-trump-frankfurt-school-brexit-critical-theory
13. Nature is Nurture
Drengson, Alan. Some Though on the Deep Ecology Movement: http://www.deepecology.org/deepecology.htm
Ewert-Krocker, Laurie. The Adolescent: Taking on the Task of Humanity—Conducting the Dialogue Between Nature and Supranature: http://www.montessori-namta.org/PDF/theadolescentandnature.pdf
Louv, Richard. Last Child in the Woods: http://richardlouv.com/books/last-child/
Tomashow, Mitchell. Bringing the Biosphere Home: http://www.mitchellthomashow.com/our-crew