One of the most common criticisms from high-school teachers, around the topic of cross-curricular implementation, is how hard it is to schedule. Everyone loves the idea of multidisciplinary activities, but other than actual interdisciplinary courses (IDC)— where two or three subjects are mandated to mix and mingle— few schools can boast of regularly achieving this gold standard of 21st century knowledge integration.
Instead of spending last summer trolling ministry websites or updating persistently nagging AQ credentials, or even skimming chapters of the latest guru on innovation and personal branding, I did what I assume most teachers need to do on their off time— I vegged out. Now, becoming a vegetable on my vacation did not mean I stopped thinking about pedagogical approaches to curriculum design, no, no, no (I am, like most lifers, a 24/7 teacher). Far from it. I did what millions of teachers do best– I turned a television show into a future lesson plan!
The show is Netflix’s superb documentary, “Chef’s Table”, which, if you haven’t already had a chance to watch, is an absolute delight of the senses and the spirit. The episode that stood out for me, and got my pedagogical flavours flowing, was the first of Season Two, with the esteemed American chef, Grant Ashatz, showcasing his experimental art project/restaurant, Alinea.
What makes the food that we do at Alinea so interesting on the outside is that we really don’t let ourselves say no to an idea.
What struck me immediately about his imaginative approach to cuisine, was how similar it was to lesson planning. He always starts with a question: In his case, “why do patrons have to eat on plates?”; in my case, “why do multidisciplinary activities have to involve other classes?”
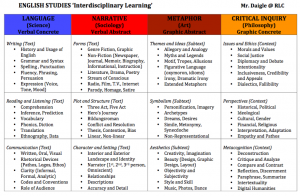
In designing an ISU for last year’s Grade 12 English class, I wanted to encourage a personalized and multidisciplinary approach by providing choice over what topic of English they wished to involve in their project. Through much discussion and co-construction (and some critical processing of my own) we came to the realization that there were at least 4 major subjects within English (Science, Sociology, Art, and Philosophy). Anyone who has taught Theory of Knowledge in an IB setting should recognize the similar pattern here. What was important to me was the senior students themselves came to this vital conclusion— that all subjects have other subjects within them, that the concept of “subject” is just a label, a way to organize information. From there the “buy-in” was easy, as most students were able to find a comfortable entry point into their project, based on a subject they enjoyed more than English, or were more skilled at. I also encouraged each student to talk to a teacher from the subject area they chose, to further deepen their research. No major rescheduling was necessary.
Grant Ashatz set the culinary world alight by challenging the basic assumptions of fine dining. He saw the simple ritual of eating to be full of potential for awe inspiring moments. Asking yourself the hard, reflective questions regarding your own practice, especially around subject stereotypes, is precisely the path towards innovation all teachers can use to reinvigorate their practice, and all students are waiting to ask. Why do we use textbooks in math? Do English students have to read the entire text? Does learning need to take place inside? Why do we need grades? Would this topic be best learned online? Do I have to write this down, can’t I just tell you?
Sometimes thinking outside the box means gaining inspiration from disciplines other than your own, other than education. Challenge the status quo. Give yourself permission to fail. Set limits to increase your creativity. These are not article links off Edutopia, they are lessons I learned from binge watching Netflix!

Eric, thanks for this post. I think that you’ve captured a great point of where great ideas come from within. It is something that I strongly believe in as well!
Tonight, I am dining with many students to talk about the lessons that we can learn from planning, seeking creating and taking part in food. It’s a potlatch, so wish me luck!
Thanks for this,
garth.
Thanks, @edaigle, for another excellent post! Your posts are always so thought-provoking and well written. Sorry for the comment delay – I’m still trying to catch up. 🙂
I think it’s great how you encouraged students to think “interdisciplinarily” without necessarily having to plan a massive, multi-teacher, scheduling nightmare. I think that the course I teach–Communications Technology–would be a good candidate for a similar approach as well. I would love to hear about the range of ISU topics that were generated by this approach.
Jen
Thanks, Jen. I’m not sure I captured everything I wanted to say about interdisciplinary. I may have to do a Part 2. I appreciate your kind comments.
One of the most successful ISU’s was for the novel Frankenstein. My Grade 12 student decided to focus on the Art and Aesthetics of the novel, mixing this assignment with his Music class to compose an actual 19th century classical romantic symphony, titled, Frankenstein, and broken into the movements of the narrative itself. He ended up getting two marks for the price of one.
Holy smokes – that’s seriously impressive! How cool.
This is exciting stuff, Eric! I love the students came to their own conclusion about the ‘interdisciplinary nature’ of all courses. I’d be interested to hear more about how you guided this discovery.
Your story about the student creating a symphony based on Frankenstein is inspiring. The fact that he was able to use this work for both English and Music speaks volumes about your ability to support your students in making those connections- that is where the real magic happens!!
It also speaks to the collaboration within departments at Rosseau- something to cherish for sure.
I was fortunate enough to teach in an integrated semester program at Outward Bound and the learning that happened in that environment was magic. While some coordination is necessary to make this kind of integrated learning happen in more traditional school, I sometimes wonder if as teachers, we make it more complicated than it needs to be. Your student is a great example of the ability to make something happen despite the (perceived?) boundaries.
Thanks for sharing and for inspiring!